Before jumping into a single line of text on your website, we’ll start by making sure your site is set up correctly. This process, called the technical SEO, allows for Google bots (and ultimately the users) to have a seamless experience on your website (This is sometimes referred to as “crawlability.”)
Crawlability and Indexing
Google bots crawl and index your website. More simply, Google gathers and analyzes the content on your website including text, images, and videos to try to understand what it is.
Although Google indexing will not directly rank your page depending on the content it sees, it makes various assumptions that it is talking about X subject which Y user is looking for. Depending on how this user interacts with the page (i.e. actively engages with it, or leaves right away), your SEO score could be influenced.
Google bots do not always index every page on your website, depending on the site’s size and crawlability. You can check to see if a page is getting crawled through the Google Search Console’s URL inspection tool.

Indexing: Increase Your Site’s Technical SEO Value
Ensure important pages are being indexed by Google:
From the Search Console > URL inspection > Verify if pages are indexed
Create an XML sitemap to help Google identify important pages on your site using tools like xml-sitemaps.com
To add your sitemap go to the Search Console > Crawl > Sitemap
*Newer platforms like Shopify, Squarespace, and various WordPress SEO Plugins automatically create a sitemap you can upload to your Search Console.
Link Structure and Architecture
Your website should be easy to explore for human users as well as bots. Structure your site so it’s easy for visitors to check out other relevant content on your site when they’re done with content on the initial search page. Doing so won’t necessarily boost your SEO directly, but good user experience does indirectly affect rankings.
Architecture: Increase Your Site’s Technical SEO Value
Keep your site to a maximum of 3-4 click levels deep.
(The more clicks needed to access a page, the less likely visitors will find it.)
Ensure your link structure is logical.
(For example, if a user wants to access your contact information, a logical pathway would be Home Page > About Us > Contact.)
Avoid link names that don’t make sense.
- Good example:
example.com/about-us - Poor example:
example.com/object?q=1563)
Webpage Loading Speed
A one-second delay in website loading time can mean 11% fewer page views, 16% decrease in customer satisfaction, and 7% loss in conversions. Google sees these factors and punishes SEO scores on websites that take too long to load.
In our experience, the biggest culprits in slowing down a website include:
- Images files that are too large
- Unused Java scripts
- Unnecessary tracking pixels for inactive campaigns
Speed: Increase Your Site’s Technical SEO Value
Check your website against Google speed standards for mobile and desktop.
Check content size by type to identify what is affecting your loading speed.
Use the suggestions provided by these tools to improve your website’s loading speed.
Mobile Accessibility
The number of people owning a smartphone increases every year, and tasks like Google searches are more commonly performed on mobile devices. More than 60% of searches are now carried out on mobile phones over desktop, and Google has taken note.
Optimizing your webpage for mobile phones directly increases your ranking with Google, so it is a must-do in 2023.
Mobile: Increase Your Site’s Technical SEO Value
Incorporate responsive design that allows your webpage to conform to mobile screen size.
Increase mobile usability by creating distinct tap targets, and avoid small content that requires pinch zooming.
Add accelerated mobile pages to change the look and functionality of a desktop website and make it more mobile-friendly.
Have mobile-formatted images and videos, which load faster.
Use Google Mobile-Friendly Test to check if a page is mobile-friendly and see the render.
Dead Links
Your website becomes more prone to avoidable mistakes over time as it is updated. It is important to keep these in check to avoid damage to your SEO score.
We’ve all seen the 404 Page Not Found error that occurs when a link that was saved previously no longer works, for any of a variety of reasons:
- The site no longer exists
- The link directory has been changed
- The page has been intentionally removed
These loose ends should be tied to let visitors know where to find the content they’re looking for.

Links: Increase Your Site’s Technical SEO Value
Code 301 Redirects for any permanent page or site moves. This allows Google to carry over the SEO value from the previous page.
Do this by using the Change of Address Tool in Google Search Console or locating the .htaccess file on platforms like WordPress.
Safely remove dead links through Google Search Console:
- Search Console > Removals > New Request
- Delete from hosting page, then upload new sitemap on Search Console
Duplicate and Updated Content
Duplicate content goes beyond just having redundant text or pictures.
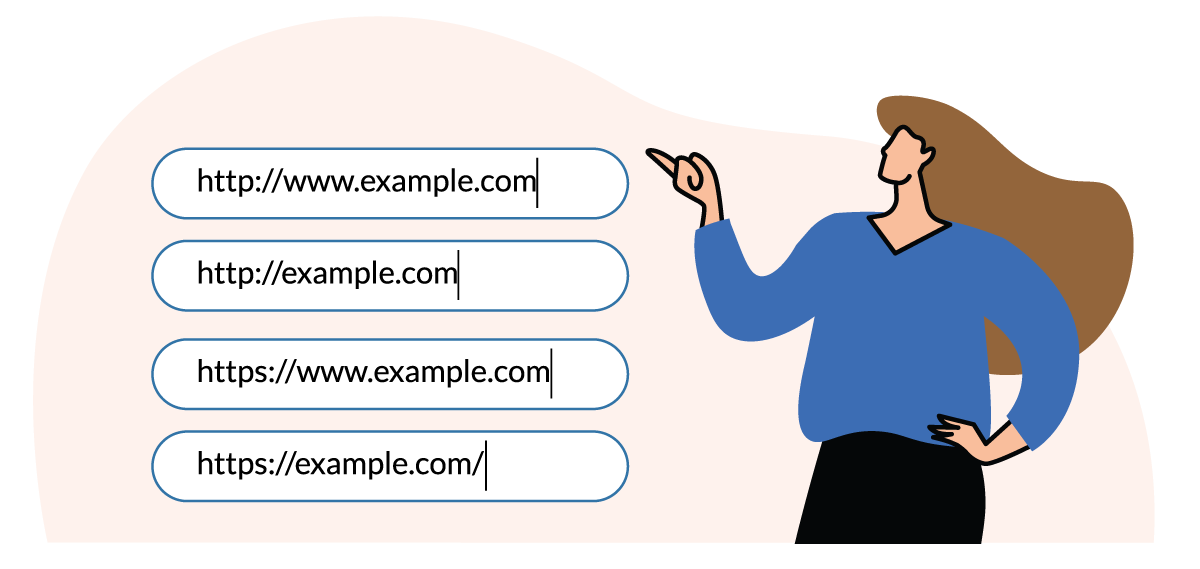
It’s fairly obvious to us that these URLs are all the same, but Google may treat them as separate sites and classify content as duplicates. (Outdated product listings and old blog posts can also show up as duplicate content.)
Re-publishing any old content with improvements can also increase SEO value. Google sees that you have made changes and will push this information out. Improvements can include:
- Website speed
- Security (http to https redesign)
- Content
- Republishing outdated blog content with current facts and trends
- Adding new ideas or materials
- Updating product listings
Content: Increase Your Site’s Technical SEO Value
Create a robots.txt in the file directory to have Google not index specific pages which may be deemed duplicate content.
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex”>
Use a canonical tag and specify to Google which page is the main or latest version. i.e. in the case above for example.com, if you update the security from http: to https:,
<link rel=”canonical” href=”https://www.example.com” />